What is Research Impact?
Research impact refers to the measurable effects, changes, or benefits that research outputs have beyond academia. It involves translating research findings into real-world applications and outcomes that positively affect society, the economy, culture, public policy, health, the environment, or quality of life.
At its core, impact can be simply defined as:
**impact = benefit**
Research impact encompasses two main categories:
- **Academic Impact:** The demonstrable contribution that excellent research makes to academic advances, across and within disciplines, including significant advances in understanding, methods, theory, application, and academic practice.
- **Wider Impact:** An effect on, change to, or benefit to the economy, society, culture, public policy or services, health, the environment, or quality of life, beyond academia.
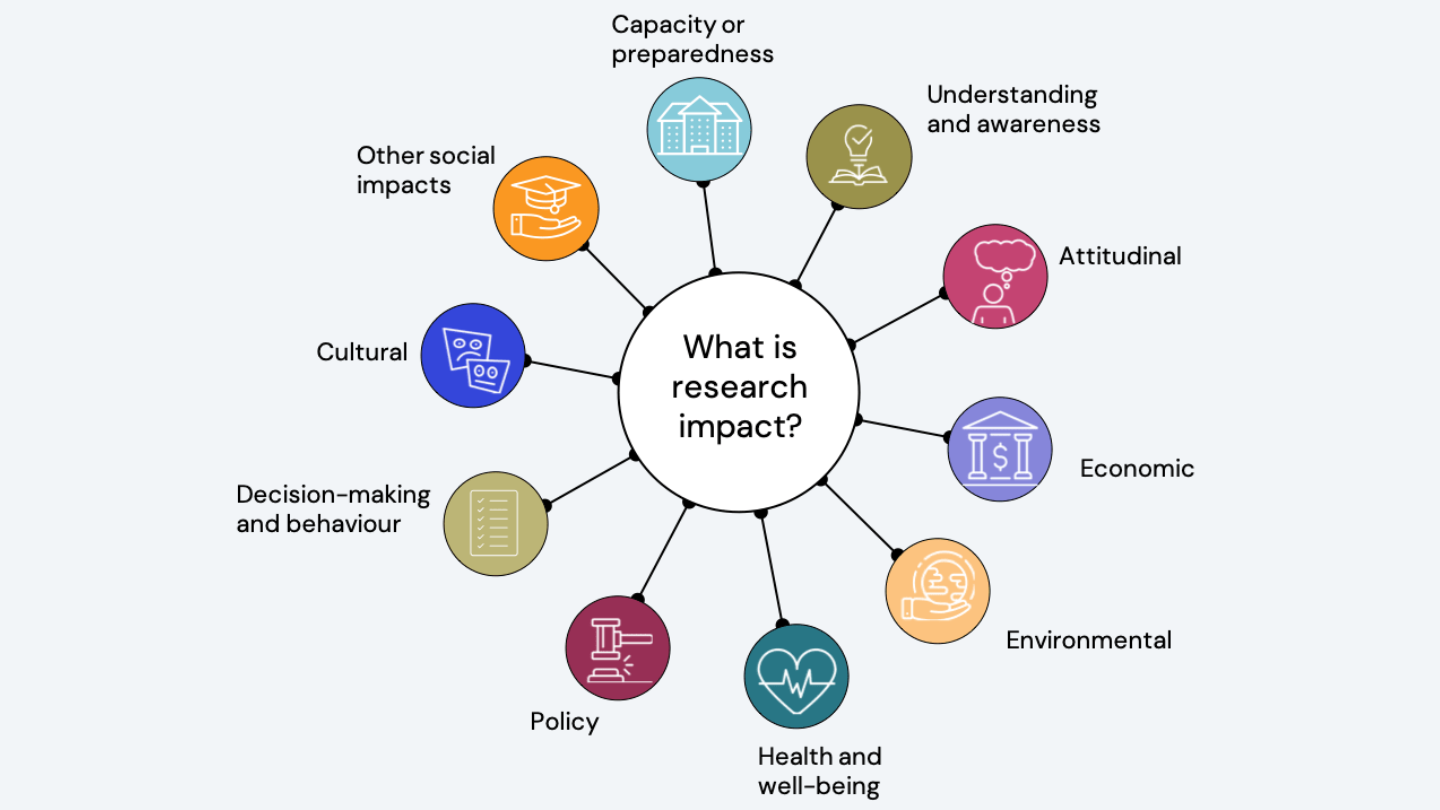
Types of wider Impact
Understanding and Awareness: Helping people better comprehend an issue
Attitudinal: Leading to changes in attitudes
Economical: Contribution to cost savings, increased revenue, profits or funding. Economic growth, job creation, productivity improvements or innovation
Environmental: Positive effects on the natural environment such as ecosystems and sustainability practices
Health and Wellbeing: Advances in medical research that lead to better healthcare practices, treatments and health outcomes
Policy: Influencing policy development, implementation and evaluation
Cultural: Changing prevailing values, attitudes, and beliefs
Social: Improvements in quality of life, social cohesion and cultural enrichment
Capacity or Preparedness: Helping individuals / groups cope with changes that may otherwise have negative impact

Why work towards Impact?
Discover the benefits and importance of Research Impact

Key Concepts in Research Impact
Check out the 3 key concepts

The Impact Journey
The impact journey is an integral part of the research cycle, click here for our 7 step process
Impact Culture
An impact culture within an institution or research community fosters an environment where research impact is valued and supported. Key elements include:
- Leadership Commitment: Strong support from institutional leaders to prioritize and promote impact activities.
- Incentives and Recognition: Rewarding researchers for their impact achievements through awards, promotions, and funding.
- Training and Resources: Providing researchers with the skills, knowledge, and tools needed to plan, execute, and measure impact.
- Collaboration and Networking: Encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration and partnerships with external stakeholders to enhance impact potential.

Impact in Funding Proposals
Many grant applications now require a detailed impact strategy. To effectively incorporate impact into funding bids, consider these key elements:
-
Understand and Define Impact Goals:
- Clearly articulate what impact means for your project and how it aligns with the funder’s priorities
- Identify both immediate and long-term impact goals
- Ensure goals are measurable using specific indicators
-
Detailed Impact Plan:
- Outline the specific activities and strategies that will be employed to achieve the desired impact
-
Identify Stakeholders and Beneficiaries:
- Determine who will benefit from your research beyond the academic community
- Engage with stakeholders early to understand their needs
-
Develop a Comprehensive Impact Pathway:
- Map out the connection between the research problem, impact goals, beneficiaries, and activities
- Use visual aids like tables and diagrams to clearly show these links
-
Co-Production and Engagement:
- Collaborate with key groups and stakeholders to co-produce impact goals
- Link activities directly to impact goals and intended beneficiaries

Useful Links
Find a full list of references and further reading
